|
|
The zatSQL.jar file contains seven publicly accessible JavaBeans. These are SqlDelete, SqlInsert, SqlSelect, SqlUpdate, SqlProcedureCall, SqlRawStatement and SqlConnection.
In addition to the beans themselves, the zat.sql package contains customizers with convenient graphical interfaces that facilitate configuration of all bean properties.
Spin supports a sophisticated connection pooling system that allows flexible configuration of shared connections to multiple data sources. Developers can take advantage of the convenient internal connection management implemented by the components or gain greater control by employing the SqlConnection component.
There are four basic steps to building database access into a Spin application:
You may not redistribute or deploy the Zat Database Components except as provided by the Zat license agreement (see the file License.txt).
Within the zatSQL.jar file there are JavaBeans Customizer classes for each of the database components. These are graphical editors which are used to configure the components and their properties. This section of the document describes the use of these customizers with each of the respective components, as well as describing how to make the components execute SQL statements.
Each of the different SQL beans has its own purpose.
| Component | SQL Equivalent | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| SqlInsert | INSERT | Create a new row. |
| SqlDelete | DELETE | Delete a row. |
| SqlUpdate | UPDATE | Change the data in an existing row or rows. |
| SqlSelect | SELECT | Search the database and/or get the data from one or more rows. |
| SqlProcedureCall | CALL | Perform a computation or arbitrary operation. |
| SqlRawStatement | Any of INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, SELECT or CALL | Perform an operation which can't be built using the components above. |
| SqlConnection | (users and passwords) | Override the internal connection management. |
The customizer for a component is launched by double-clicking on the component in the capsule outline or using the Edit Custom menu item in the Actor menu. The Actor menu can also be brought up by right clicking the component in the outline.
The first step in configuring a database component is to specify the data source on which the component will be operating. This involves selecting the name of the connection which will be used for editing and execution. For example, when adding a new instance of SqlInsert to a capsule, the user is presented with the following dialog when the editor is brought up.
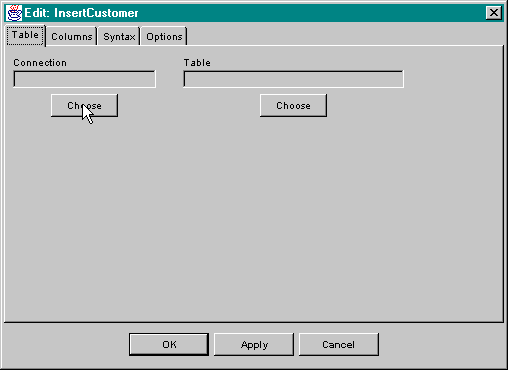
Clicking on the Choose button below the Connection field brings up a dialog allowing the selection of a connection name from a list of names which are set up in the zatsql.properties file. The dialog looks like this:

Highlight the desired connection name and press the Ok button. The
selected connection name will now appear in the Connection field.
The next step is to select a database object that the component will operate on. For the SqlDelete, SqlInsert and SqlUpdate components, this will be a single table. The SqlSelect component allows more than one table to be accessed using joins. In the case of the SqlProcedureCall component, the user selects a stored procedure. Continuing on with our SqlInsert example, the user specifies a table by pressing the Choose button beneath the Table field. This action brings up a dialog to choose a table.
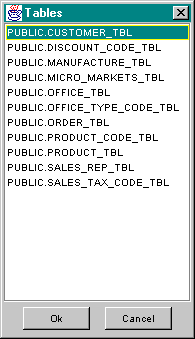
Select the desired table and press the ok button. The component editor will now look something like this:
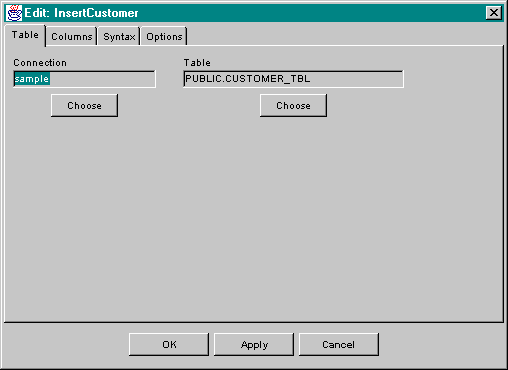
The SqlInsert, SqlSelect, and SqlUpdate components require that the columns accessed during execution are specified. For SqlInsert and SqlUpdate, the selected columns are those to which data will be written in the database. For SqlSelect, the selected columns are those which will be included in rows returned in a result set.
In the case of SqlInsert and SqlUpdate, columns are specified using the Columns tab page of the respective editor. The Columns tab page looks like this:
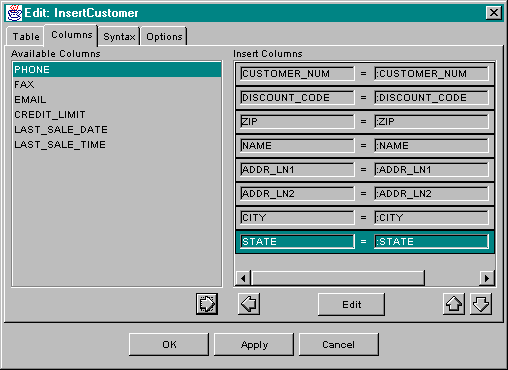
To include a column, select it in the Available Columns list and press the
add column ![]() button. The column will be moved into the Insert Columns list. A
column can be removed and returned to the Available Columns by selecting the
column and pressing the remove column
button. The column will be moved into the Insert Columns list. A
column can be removed and returned to the Available Columns by selecting the
column and pressing the remove column ![]() button. The ordering of
columns can be changed using the up and down buttons,
button. The ordering of
columns can be changed using the up and down buttons, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
For SqlInsert and SqlUpdate to perform any useful work, column values must be provided, typically by using the setParameterXX() methods. When columns are added to the component using the add column button, they are given a parameter name equal to the column name by default. This means that prior to execution of the SQL statement, a method call such as setParameterString("CITY", "Portland") should be invoked to set the column value. Values for columns can be set using the setParameterXX() methods, or by typing SQL syntax directly using the Edit Column dialog. The manner in which column values are set can be modified by selecting the column and pressing the Edit button. This action brings up the following dialog:
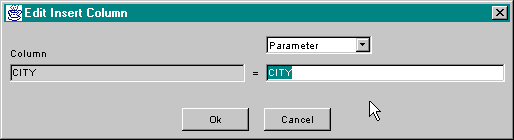
In the case above the column value will be set using a named parameter. The parameter could also be set by selecting SQL Syntax in the popup above the edit field and typing syntax into the field below. This would appear as:

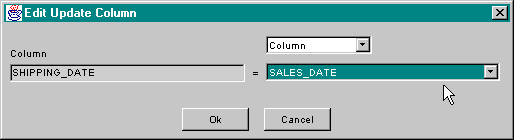
In a SqlUpdate component, one additional option is available: The value of an update column can be set to the value of another column. This type of column value is shown below.
While statement-type database components are being edited, the generated SQL syntax can be viewed at any time by switching to the Syntax tab page:
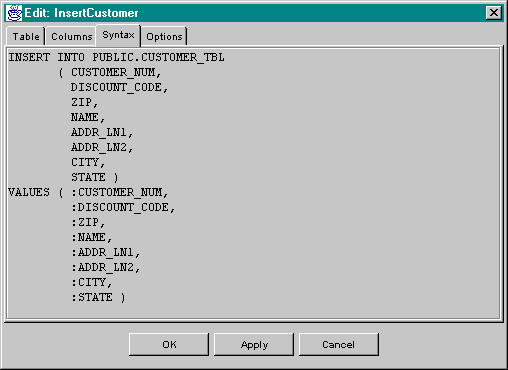
Items with colons (:) in front of them are named parameters. These items
are replaced with actual values by Spin behaviors via the
setParameterXX() methods.
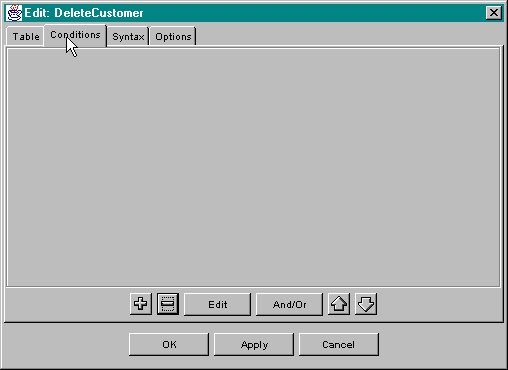
Conditions are used to control the scope of operation of delete, select and update operations. The method of editing conditions in the Spin database components is identical for the three components which make use of conditions. These conditions become part of the WHERE clause in the SQL syntax generated by the component. The first step in configuring conditions is to select the Conditions tab on the customizer. To illustrated the process we will use a SqlDelete component which will be configured to delete row(s) from the CUSTOMER_TBL table. At first the editor appears as:
A condition can be added by pressing the add button, ![]() . Pressing this button brings
up the Edit Condition dialog:
. Pressing this button brings
up the Edit Condition dialog:
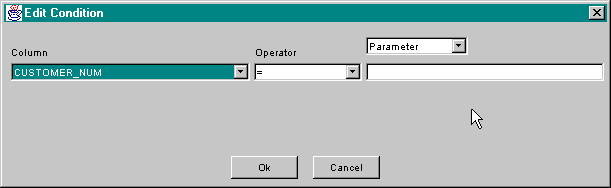
Editing a condition involves graphically creating an expression which consists of a left hand operand, an operator, and a right hand operand. The left hand operand is a column. The standard SQL relational operators are supported. These operators are:
| = | equals |
| <> | does not equal |
| < | less than |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| > | greater than |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| LIKE | matches string |
| NOT LIKE | does not match |
| IN | is in a set of values |
| NOT IN | is not in a set of values |
| IS NULL | column contains no value |
| IS NOT NULL | column contains a value |
The operator is selected using the Operator popup.
The right hand operand may be a parameter, another column, or SQL syntax. The kind
of right hand operand to be used is selected using the popup above the right
hand operand. Like the Edit Column dialog, if
the Parameter option is used, values must be provided by using one of the
setParameterXX() methods before execution of the statement.
The order in which results are returned by a SELECT can be specified in the
Sorts tab of the SqlSelect editor. A dialog to edit a sort can be brought up by
using the add button, ![]() ,
to create a new sort, or the Edit button to edit an
existing sort.
,
to create a new sort, or the Edit button to edit an
existing sort.
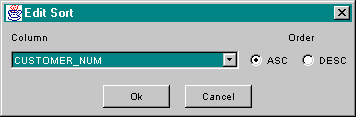
The collation order of the sort can be either ascending or descending, and is set by selecting the ASC or DESC radio button, respectively.
The ordering of multiple sorts can be changed using the up and down buttons, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
When more than one table must be accessed by a SqlSelect component it is
necessary to create joins to link the related tables. In the SqlSelect editor,
joins are edited from the Joins tab. Press the add button, ![]() , to create a new join. This action
brings up the join editing dialog as shown below:
, to create a new join. This action
brings up the join editing dialog as shown below:
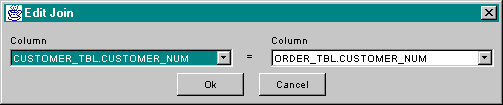
Select the columns to be joined and press the Ok button. The dialog will disappear bringing the Joins tab of the editor back to the top of the display:

The Formats tab of the SqlSelect editor shown below displays the returned data columns along with type and format information for each.

For each column in the list, the following information is displayed: the column name, the JDBC type, the Java type, and the format. The Java type is the type that will be used to represent the column value after it has been fetched from the database. Type conversions to the target Java type are performed automatically by the database components. The format is used to specify the formatting of a column value if it converted to string form, either during retrieval or using a method such as getColumnString(). The Java type and string format can be edited by selecting the desired column and pressing the Edit button. This action brings up a dialog which looks like:
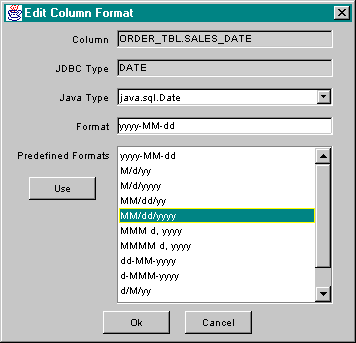
Using this dialog, the Java type to be used for retrieved values can be set using the Java Type popup. Usually the default type is the best to use. Formats can be selected from a list of predefined formats or by typing the format string into the Format edit field using standard Java notation.
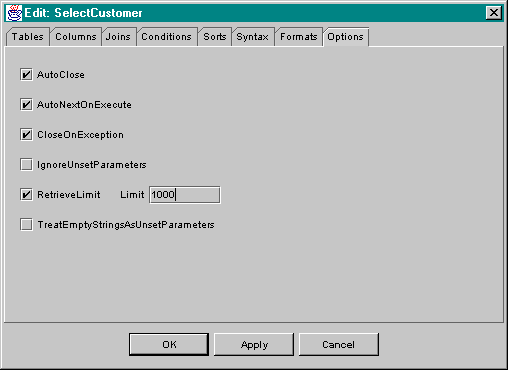
The SQL statement-related database components; SqlDelete, SqlInsert, SqlSelect, SqlUpdate, SqlProcedureCall, and SqlRawStatement, support a set of options which are set using the Options tab of the respective editor. The Options tab for the SqlSelect editor is show below as SqlSelect supports the full complement of options. Details on the meaning of these options is presented in the section entitled The Classes.
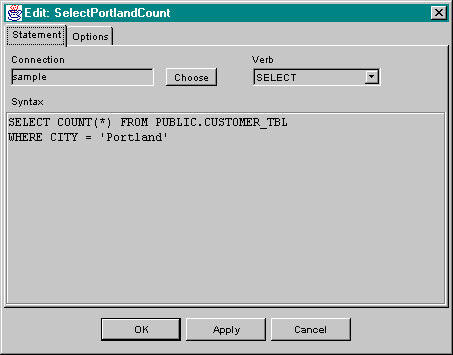
An example of an editor for SqlRawStatement is shown below. The appropriate verb should be selected using the Verb popup and the syntax of a single SQL statement should be typed into the text area. The example shown would return a count of customers in Portland.
All the components except SqlConnection represent SQL statements which need to be sent to the database for execution. To make a statement execute, a Spin Behavior should be created which invokes the execute() method of the component.
As discussed above, statements with conditions (with a WHERE clause) that are using named parameters, should have the value of those parameters set by invoking setParameterXX() methods on the object.
For SqlDelete, SqlInsert, and SqlUpdate components, once the execute() method has been invoked, nothing more needs to be done, unless the AutoClose and/or CloseOnException options have not been used, in which case the component's close() method should be invoked.
SqlSelect components are designed to return data to the Spin capsule one row at a time. For each row that matched the condition of the SELECT statement, a rowRetrieved event is generated. A Spin Behavior should be created which is activated by this event. That behavior, or others triggered along with it, can retrieve data from the row one column at a time, using getColumnXX() methods, or the entire row can be retrieved as a HashTable using getColumnValuesAsHashtable().
After all behaviors triggered by the rowRetrieved event
have executed, the SqlSelect component sets up the
next row of data and generates a new rowRetrieved event.
Finally, a noMoreRows event is generated.
The properties for a SqlConnection component are edited using an editor as shown below.
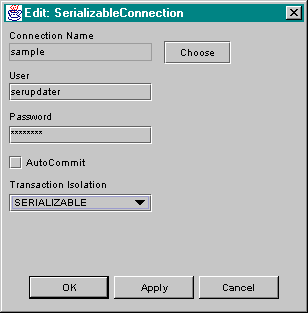
To make use of a SqlConnection component, a few Spin behaviors should be created to invoke the following methods on the SqlConnection:
Other Spin behaviors should be inserted which invoke the setSqlConnection() method on other components to cause those components to use this connection object.
In order to make efficient and tunable use of system resources in concurrent multi-user environments, the Zat database components make use of a connection pooling method. A configurable pool of connections is managed by supporting classes that make these connections available to components. These connections are created on demand and may be shared among several database components requiring connectivity to one data source.
There are two ways in which a database component obtains a connection in Spin: internally and externally.
The most convenient way of dealing with connections is to allow the component to obtain the connection internally. When a statement is configured during authoring, the connectionName property is set to indicate which pool should be used by the component to obtain a connection. When the component is called upon to do work, it handles obtaining the connection transparently, requiring no further work by the developer. By default, the database components use internal connection management.
Sometimes a greater deal of control is required than that provided by internal connection management. For example, when multiple database components need to use the same connection due to transaction ordering and/or interdependency requirements, internal connection management is not sufficient. In such a context, the database components allow external connection management in which the connection object is supplied to the component using the setSqlConnection() method to pass a SqlConnection object to the database component.
The connection manager is configured using the zatsql.properties file. In the Spin development environment this file is located in the Spin directory. When a project is deployed on a Web server, this file must be located in the "current working directory" of the program that executes servlets.
The location of the current working directory depends on the operating system and Web server program (or servlet engine) running on your Web server. If you do not know the working directory for your Web server, Spin includes a servlet called printprops in the exampleservlets subdirectory. From Spin, save this servlet as a jar file and deploy it onto your Web server, then execute it and find the value of the user.dir property.
All Spin servlets running on the same Web server can share a single zatsql.properties file.
A separate connection pool with a unique name must be defined in this file for each database that the Spin application will communicate with. Additionally, a separate pool must be defined for each user/password combination that the application will use to identify itself as it connects to each database.
Here is an example file which will be used to explain the settings which configure the connection manager.
drivers=com.pointbase.jdbc.jdbcUniversalDriver
logfile=zatsql.log
defaultConnectionName=sample
sample.url=jdbc:pointbase://localhost/sample
sample.maxconn=2
sample.user=public
sample.password=public
sample.transactionIsolation=READ_COMMITTED
The remaining properties are specific to each individual pool and take the form poolname.property=value. These properties are as follows.
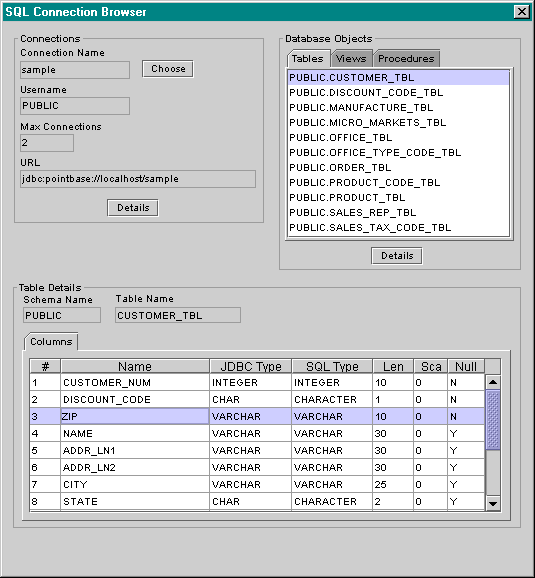
Spin provides a window for viewing information about the data sources that have been configured using the zatsql.properties file. This window is displayed by selecting the SQL Connections... menu item in the File menu.
Spin comes bundled with an evaluation copy of the PointBase relational database server and client Java software, allowing development of database enabled applications without needing any software not included with Spin. (Note: You may not deploy a PointBase server without first purchasing a fully licensed version from PointBase -- the evaluation server is provided for testing and development purposes.) The server may be executed from within Spin by setting the PointBaseServerLoadsAtStart property to true in the General tab of the Edit Preferences dialog in Spin. When this property is changed, Spin must be restarted for the change to take effect. The database server may also be executed as a separate application using the PointBase Server menu shortcut which is created during the installation of Spin.
The Zat database components provide a easy to use layer of functionality wrapping the JDBC API. There are six components which represent SQL statements and one which represents a connection to a data source. All of the components and supporting classes are in the package zat.sql.
The recommended way to configure a Spin database component is by utilizing the component's associated customizer, a graphical interface for setting the component's properties and configuration. The customizer for a database component can be obtained by double-clicking on the component in the Spin capsule outline or selecting Edit-Custom from the Actor menu. The Actor menu can also be brought up by right clicking the component in the outline.
For a database component to perform any useful work with a database, a connection to the database is necessary. Spin provides a connection pooling system which is discussed in greater detail above.
The first two classes in this section are SqlAbstractStatement and SqlProgrammedStatement statement. Both these classes are abstract, but contain public methods which are callable in subclass instances. Here is a visual representation of the class hierarchy:
SqlAbstractStatement
|
+----SqlProcedureCall
|
+----SqlRawStatement
|
+----SqlProgrammedStatement
|
+----SqlDelete
|
+----SqlInsert
|
+----SqlSelect
|
+----SqlUpdate
SqlConnection
Extends java.lang.object
SqlAbstractStatement is the superclass of SqlProgrammedStatement, SqlProcedureCall and SqlRawStatement. Subclasses of SqlAbstractStatement represent statements sent to the database for execution.
public void close()
Frees the resources of the statement.
public void execute()
Executes the statement.
Extends zat.sql.SqlAbstract
SqlProgrammedStatement is the superclass of SqlDelete, SqlInsert, SqlSelect and SqlUpdate.
public void resetParameters()
This method resets all parameter values to null and and sets each parameter
object's isSet flag to false.
public void setMatchingParameterValues(Hashtable params)
Sets parameters from a hashtable. Parameter values can be grouped together in a hashtable as parameter name, value pairs. This method iterates through the keys in the hashtable. When a key matches an existing parameter name, the parameter is set to the associated value.
Parameters:
params - a hashtable
containing the parameter name, value pairs
public void setParameterBlob(String name, SqlBlob value)
Sets the designated parameter to a SqlBlob value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterBoolean(String name, boolean value)
Sets the designated parameter to a boolean value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterByte(String name, byte value)
Sets the designated parameter to a byte value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterClob(String name, SqlClob value)
Sets the designated parameter to a SqlClob value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterDate(String name, java.sql.Date value)
Sets the designated parameter to a java.sql.Date value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterDouble(String name, double value)
Sets the designated parameter to a double value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterFloat(String name, float value)
Sets the designated parameter to a float value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterInt(String name, int value)
Sets the designated parameter to an int value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterLong(String name, long value)
Sets the designated parameter to a long value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterObject(String name, Object value)
Sets the designated parameter to an Object value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterShort(String name, short value)
Sets the designated parameter to a short value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterString(String name, String value)
Sets the designated parameter to a String value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterTime(String name, java.sql.Time value)
Sets the designated parameter to a java.sql.Time value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterTimestamp(String name, java.sql.Timestamp value)
Sets the designated parameter to a java.sql.Timestamp value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
Icon ![]()
Extends SqlProgrammedStatement
SqlDelete is used to delete rows of data in a database.
executionCompleted - fired when the SQL command has completed execution
Icon ![]()
Extends SqlProgrammedStatement
SqlInsert is used to insert new rows of data into a database.
executionCompleted - fired when the SQL command has completed execution
Icon ![]()
Extends SqlProgrammedStatement
SqlSelect is used to retrieve rows of data from a database.
executionCompleted - fired when the SQL command has completed execution
noMoreRows - fired when the next() method is invoked and there are no more rows available to be retrieved
retrieveLimitReached - fired when the number of rows retrieved has reached the count set in the retrieveLimit property.
rowRetrieved - fired after a row has been retrieved
public boolean columnWasNull(int index)
Returns whether or not a column was null.
Parameters:
index
the index of the column (1 - n)
Return:
true if column was
null, false
otherwise
public boolean columnWasNull(String name)
Returns whether or not a column was null.
Parameters:
name
-the name of the column
Return:
true if column was
null, false
otherwise
public SqlBlob getColumnBlob(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public SqlBlob getColumnBlob(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public boolean getColumnBoolean(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public boolean getColumnBoolean(String name)
Parameters:
name
- the name of the column
Return:
the value of the column
public byte getColumnByte(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index of the
column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public byte getColumnByte(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public SqlClob getColumnClob(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index of the
column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public SqlClob getColumnClob(String name)
Parameters:
name
- the name of the column
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Date getColumnDate(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index of the
column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Date getColumnDate(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public double getColumnDouble(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public double getColumnDouble(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public float getColumnFloat(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public float getColumnFloat(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public int getColumnInt(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public int getColumnInt(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public long getColumnLong(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public long getColumnLong(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public Object getColumnObject(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index of the
column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public Object getColumnObject(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public short getColumnShort(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public short getColumnShort(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public String getColumnString(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public String getColumnString(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Time getColumnTime(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Time getColumnTime(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Timestamp getColumnTimestamp(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Timestamp getColumnTimestamp(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public boolean columnWasNull(String name)
Returns whether or not a column was null.
Parameters:
index
the index of the column 1-n
Return:
true if column was
null, false
otherwise
public Hashtable getColumnValuesAsHashtable()
Places all column values in the most recently fetched row into a hashtable with the column names as keys.
Return:
a hashtable containing column name, value pairs from the current
row
Icon ![]()
Extends SqlProgrammedStatement
SqlUpdate is used to update rows of data in a data source.
executionCompleted - fired when the SQL command has completed execution
Icon ![]()
Extends SqlAbstractStatement
SqlProcedureCall is used to invoke stored procedures in the database.
executionCompleted - fired upon completion of execution
noMoreRows - fired when the next() method is invoked and there are no more rows available to be retrieved
retrieveLimitReached - fired when the number of rows retrieved has reached the count set in the retrieveLimit property.
rowRetrieved - fired after a row has been retrieved
public boolean getColumnBoolean(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public boolean getColumnBoolean(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public byte getColumnByte(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public byte getColumnByte(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public byte[] getColumnBytes(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public byte[] getColumnBytes(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Date getColumnDate(int index)
Parameters:
index
the index of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Date getColumnDate(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public double getColumnDouble(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public double getColumnDouble(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public float getColumnFloat(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public float getColumnFloat(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public int getColumnInt(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public int getColumnInt(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public long getColumnLong(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public long getColumnLong(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public Object getColumnObject(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public Object getColumnObject(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public short getColumnShort(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public short getColumnShort(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public String getColumnString(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public String getColumnString(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Time getColumnTime(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Time getColumnTime(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Timestamp getColumnTimestamp(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Timestamp getColumnTimestamp(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public Hashtable getColumnValuesAsHashtable()
Places all column values in the most recently fetched row into a hashtable with the column names as keys.
Return:
a hashtable containing column name, value pairs from the current
row
public void setMatchingParameterValues(Hashtable params)
Sets parameters from a hashtable. Parameter values can be grouped together in a hashtable as parameter name, value pairs. This method iterates through the keys in the hashtable. When a key matches an exiting parameter name, the parameter is set to the associated value.
Parameters:
params
a hashtable containing the parameter name, value pairs
public void setParameterBlob(String name, SqlBlob value)
Sets the designated parameter to a SqlBlob value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterBoolean(String name, boolean value)
Sets the designated parameter to a boolean value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterByte(String name, byte value)
Sets the designated parameter to a byte value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterClob(String name, SqlClob value)
Sets the designated parameter to a SqlClob value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterDate(String name, java.sql.Date value)
Sets the designated parameter to a java.sql.Date value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterDouble(String name, double value)
Sets the designated parameter to a double value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterFloat(String name, float value)
Sets the designated parameter to a float value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterInt(String name, int value)
Sets the designated parameter to an int value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterLong(String name, long value)
Sets the designated parameter to a long value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterObject(String name, Object value)
Sets the designated parameter to an Object value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterShort(String name, short value)
Sets the designated parameter to a short value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterString(String name, String value)
Sets the designated parameter to a String value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterTime(String name, java.sql.Time value)
Sets the designated parameter to a java.sql.Time value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
public void setParameterTimestamp(String name, java.sql.Timestamp value)
Sets the designated parameter to a java.sql.Timestamp value.
Parameters:
name
- the name of the parameter
value - the value
Icon ![]()
Extends SqlAbstractStatement
This component allows any valid SQL syntax to be submitted to the database. This removes any limitation on the kind of SQL commands which can be used such as complex nested statements or groupings not supported by the graphically configured components. The component, in effect, provides a convient general wrapper to the JDBC API to execute database statements.
executionCompleted - fired upon completion of execution
noMoreRows - fired when the next() method is invoked and there are no more rows available to be retrieved
retrieveLimitReached - fired when the number of rows retrieved has reached the count set in the retrieveLimit property.
rowRetrieved - fired after a row has been retrieved
public boolean getColumnBoolean(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public boolean getColumnBoolean(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public byte getColumnByte(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public byte getColumnByte(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public byte[] getColumnBytes(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public byte[] getColumnBytes(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Date getColumnDate(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Date getColumnDate(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public double getColumnDouble(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public double getColumnDouble(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public float getColumnFloat(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public float getColumnFloat(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public int getColumnInt(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public int getColumnInt(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public long getColumnLong(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public long getColumnLong(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public Object getColumnObject(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public Object getColumnObject(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public short getColumnShort(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public short getColumnShort(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public String getColumnString(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public String getColumnString(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Time getColumnTime(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Time getColumnTime(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Timestamp getColumnTimestamp(int index)
Parameters:
index - the index
of the column (1 - n)
Return:
the value of the column
public java.sql.Timestamp getColumnTimestamp(String name)
Parameters:
name - the name of
the column
Return:
the value of the column
public void setParameterBoolean(int index, boolean value)
Sets the designated parameter to a boolean value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterByte(int index, byte value)
Sets the designated parameter to a byte value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterBytes(int index, byte value)
Sets the designated parameter to a byte[] value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterDate(int index, java.sql.Date value)
Sets the designated parameter to a java.sql.Date value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterDouble(int index, double value)
Sets the designated parameter to a double value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterFloat(int index, float value)
Sets the designated parameter to a float value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterInt(int index, int value)
Sets the designated parameter to an int value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterLong(int index, long value)
Sets the designated parameter to a long value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterObject(int index, Object value)
Sets the designated parameter to an Object value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterShort(int index, short value)
Sets the designated parameter to a short value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterString(int index, String value)
Sets the designated parameter to a String value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterTime(int index, java.sql.Time value)
Sets the designated parameter to a java.sql.Time value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
public void setParameterTimestamp(int index, java.sql.Timestamp value)
Sets the designated parameter to a java.sql.Timestamp value.
Parameters:
index - the index of the
parameter (1 - n)
value - the value
Icon ![]()
Extends Object
SqlConnection is Spin's representation of a database connection. This component wraps a JDBC connection obtained from the connection pool and adds functionality used by the database components. Quite often the developer need not be concerned with this component because of the intrinsic internal connection management implemented by the database components. However when greater control is necessary, the developer can make use of SqlConnection.
| TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED | 1 | Dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads can occur. |
| TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED | 2 | Dirty reads are prevented; non-repeatable reads and phantom reads can occur. |
| TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ | 4 | Dirty reads and non-repeatable reads are prevented; phantom reads can occur. |
| TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE | 8 | Dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads are prevented. |
none
public void commit()
Commits the work done by the connection since the last commit or rollback.
public void connect()
Connects to the database
public void disconnect()
Frees the connection. If the connection uses an application-supplied
username and password, the connection is closed at the JDBC level.
Otherwise, the connection is returned to the pool it came from.
public void rollback()
Rolls back all changes to the database since the last commit or rollback.